Befor Reading The BLOG please see my video
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-o6Gf2fO7at8lLZnMbhJrwPZId1sXsBI/view?usp=sharing
In the modern world, technology has seamlessly integrated into various aspects of our lives, making our experiences more comfortable and efficient. Among the many innovations that have emerged, temperature sensors stand out as a fundamental tool used in countless applications. Whether it's monitoring weather conditions, regulating industrial processes, or ensuring the optimal functioning of electronic devices, temperature sensors play a role in maintaining our surroundings.Temperature sensors, as the name suggests, are devices designed to measure temperature. They are engineered to detect and convert temperature that changes into electrical signals, which can be further analyzed or utilized by other systems. These sensors rely on various physical properties, such as electrical resistance, voltage, or electromagnetic radiation, to accurately determine temperature levels.Temperature is one of the most fundamental and essential physical parameters we encounter in our daily lives. From monitoring weather conditions to controlling industrial processes, accurate temperature measurement is crucial for various applications. One of the key tools that enable us to achieve this precision is the temperature sensor. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of temperature sensors, understanding their types, working principles, and diverse applications.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs): RTDs are made of pure metals, such as platinum, which exhibit a predictable change in electrical resistance with temperature. They provide highly accurate measurements and are commonly used in scientific and industrial applications.
Thermistors: Thermistors are temperature sensors that use semiconductor materials with a high temperature sensitivity. They are of two types: Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors, where resistance increases with temperature, and Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors, where resistance decreases with temperature.
Digital Temperature Sensors: These sensors provide digital outputs, often using protocols like I2C or SPI. They are integrated with microcontrollers or other digital devices, making them ideal for use in modern electronics.
The field of temperature sensor continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology. Miniaturization, improved accuracy, wireless connectivity, and the integration of sensors into smart devices are some of the ongoing trends. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), temperature sensors are becoming an integral part of smart homes, wearable devices, and industrial automation systems.
The working principle of temperature sensors varies depending on the type of sensor used. However, most temperature sensors rely on the fundamental property that certain physical characteristics of materials change with temperature.
Thermocouples work based on the Seebeck effect, where a voltage is generated across the junction of two dissimilar metals in response to a temperature gradient.
RTDs utilize the temperature-dependent change in electrical resistance of pure metals.
Thermistors use the temperature sensitivity of semiconductor materials to measure temperature.
IR temperature sensors detect and measure the thermal radiation emitted by objects, converting it into temperature values.
Applications of Temperature Sensors:
Weather Forecasting: Temperature sensors play a crucial role in weather monitoring and forecasting. By collecting temperature data from various locations, meteorologists can analyze weather patterns, predict climate changes, and issue accurate forecast.
Medical and Healthcare: Temperature sensors are used extensively in medical applications, including thermometers, patient monitoring systems, incubators, and laboratory equipment. Accurate temperature measurement is essential for diagnosis, treatment, and research purposes
Food Industry: Temperature sensors are used for food safety and storage, ensuring perishable goods are stored at the right temperatures.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): They help regulate indoor temperature for comfort and energy efficiency.
In research and development, temperature sensors enable scientists and engineers to conduct experiments, study material behavior, and innovate new technologies by providing precise and reliable temperature data.
KINDLY SEE MY PROJECT FROM THE GIVEN BELOW LINK:
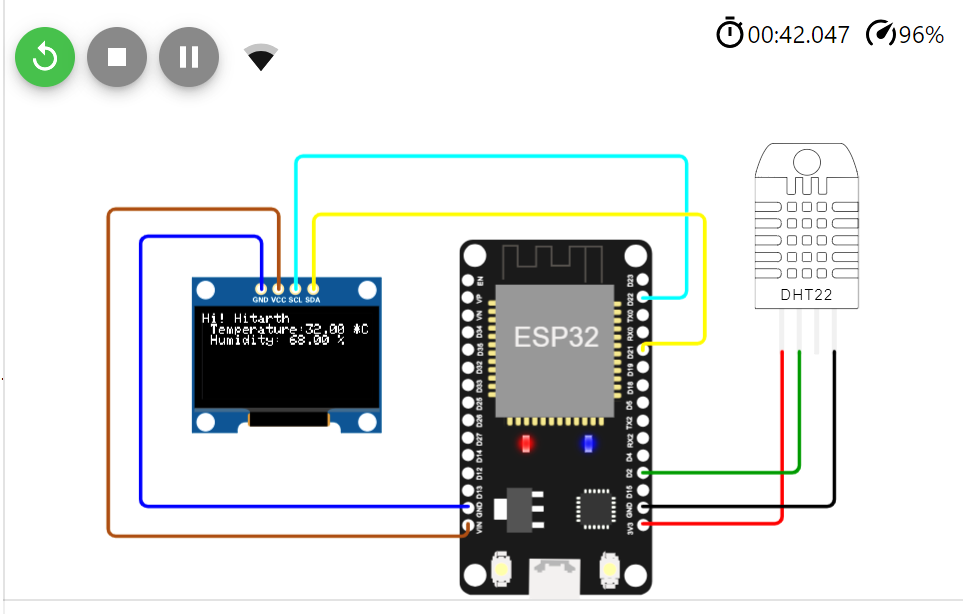
https://wokwi.com/projects/367947768115960833
IF YOU WANT TO SEE MORE ABOUT CLICK ON THE GIVEN LINK:
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/19-F4YQNWajJEsj903hIu3ytePKqja5lRJIY1K5UOHrQ/edit?usp=sharing
By-Hitarth Garg,Salwan Public School Gurugram